Education Corner
Learn how medical cannabis can support your health and wellness journey.
Understanding Cannabinoids
Cannabis contains a variety of naturally occurring chemical compounds known as cannabinoids. These compounds interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system. Each cannabis product lists the concentration of key cannabinoids, most commonly:

THC is one of the main cannabinoids in cannabis and is commonly listed as the dominant compound in many products. Canadian labels show THC and Total THC, indicating the active and potential amounts. THC levels vary by product and are expressed in mg/g or mg per unit.

CBD is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid found in many cannabis products. It’s commonly present in CBD-dominant or balanced formulations. Like THC, labels show CBD and Total CBD, providing both raw and heat-activated values. It’s measured in mg/g or mg per unit

Cannabis may also contain minor cannabinoids in small amounts. These include CBN, CBG, CBC, and others, which contribute to the product’s overall cannabinoid profile. They’re not always listed on packaging but may appear in detailed lab reports or certificates of analysis.
What are Terpenes?
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in cannabis and many other plants. In cannabis, they are produced in the trichomes, the same structures that create cannabinoids like THC and CBD. Terpenes are responsible for the distinct scents and flavours of different cultivars, contributing to aromas such as citrus, pine, earth, spice, or floral notes.
Here are some of the most commonly found terpenes:
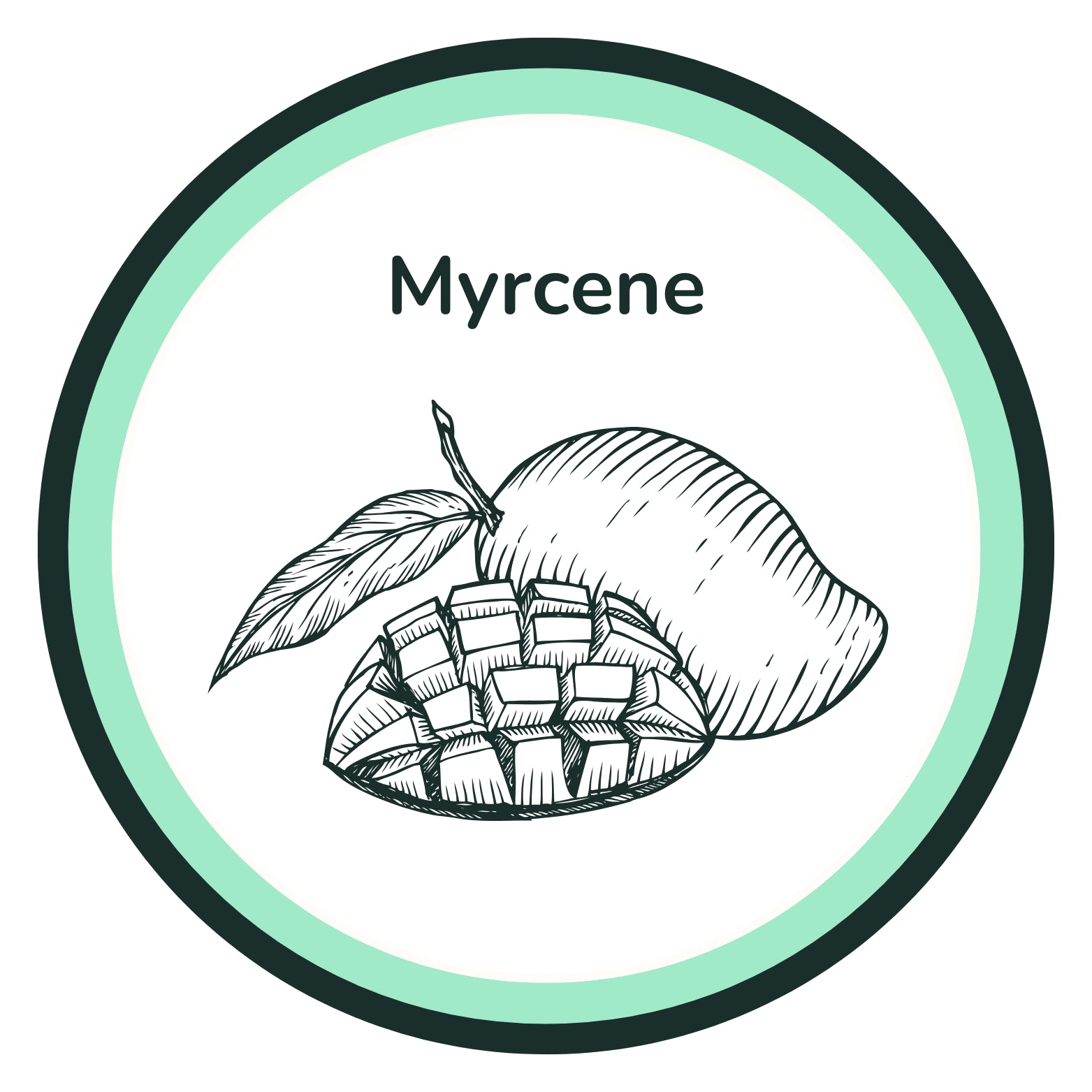
Earthy, musky, herbal — commonly found in mangoes, hops, and lemongrass.

Bright, citrus-like aroma — also present in lemons, oranges, and other citrus fruits.
Sharp, pine-like scent — naturally found in pine needles, rosemary, and basil.
Spicy, peppery aroma — also found in black pepper, cloves, and cinnamon.

Floral and lavender-like — found in lavender, coriander, and some mint varieties.
Fresh, herbal, and slightly sweet — present in apples, nutmeg, and lilacs.

Woody and earthy — commonly found in hops, coriander, and cloves
Sweet, herbal, and sometimes citrusy — found in mint, basil, and orchids.
Light, floral, and mildly sweet — found in chamomile and some cosmetic products.
Cannabis Plant Types
Cannabis products are commonly described using terms like Indica, Sativa, and Hybrid. These terms are based on the botanical characteristics and growth patterns of different cannabis plants. While widely used in product descriptions, they are not scientific or regulatory classifications.

Sativa
Sativa is generally used to describe plants with narrow leaves and a taller growth habit, associated with the Cannabis sativa species. These plants may have longer flowering times and are commonly grown in warmer climates.

Indica
Indica typically refers to plants with broad leaves and a shorter, bushier structure. This term originally described Cannabis indica varieties and is often used to identify certain physical features of the plant during cultivation.

Hybrid
Hybrid describes cannabis cultivars that result from crossbreeding indica and sativa varieties. Hybrids can exhibit a wide range of physical traits, depending on their genetic lineage and how they are cultivated.
Our Product Formats
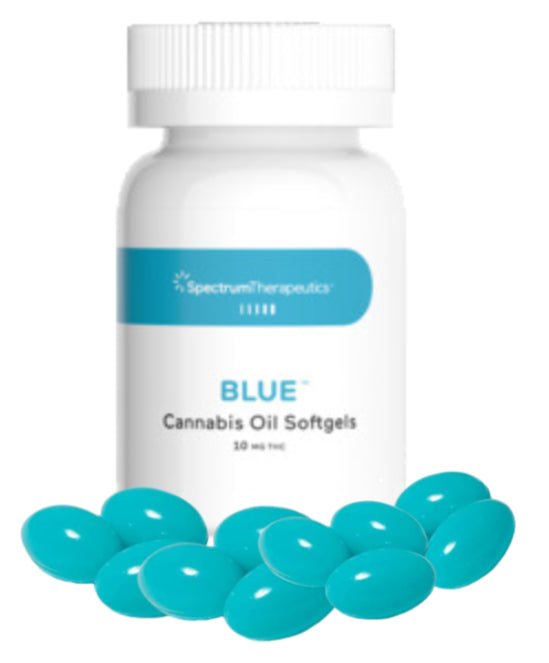
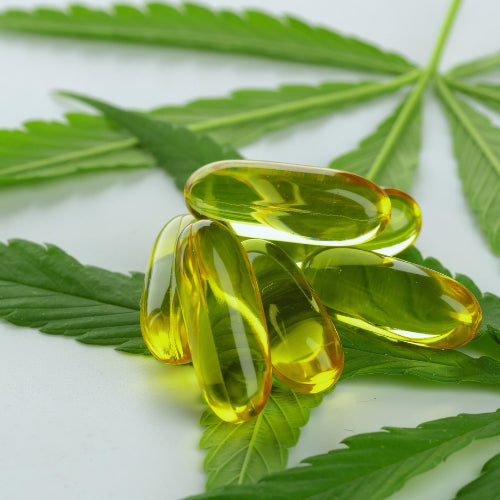
Softgels
Softgels are filled with extracted cannabis resin dissolved in a food-grade carrier oil in a dosed form. They offer you a convenient and discreet option for your medication.

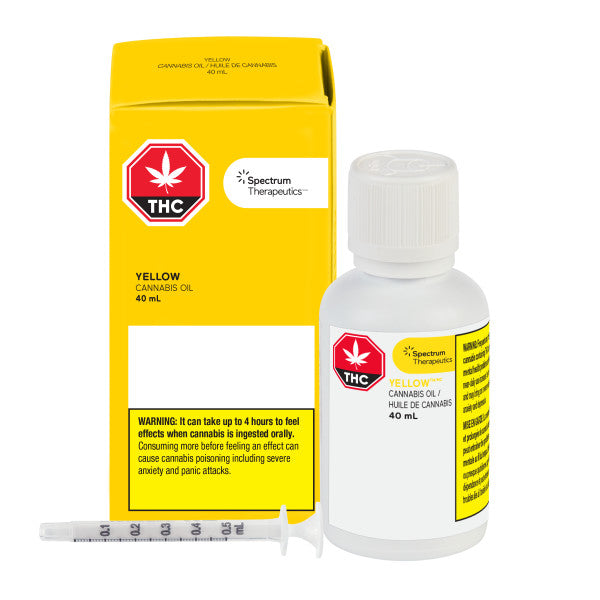
Cannabis Oil
Concentrated cannabis resin, containing cannabinoids and other active compounds, is extracted from cannabis flowers that have undergone thermal decarboxylation, then diluted with a food-grade carrier oil to make a product for you to take orally from a syringe. This allows you to know exactly how much THC and CBD you are taking in each dose.

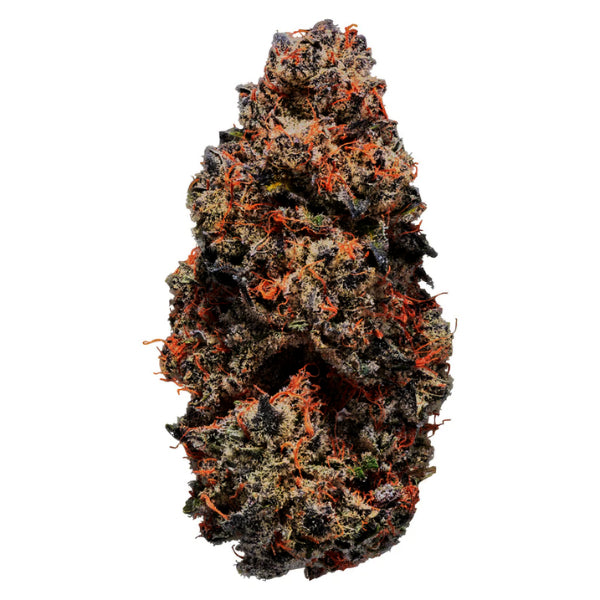
Dried Flower
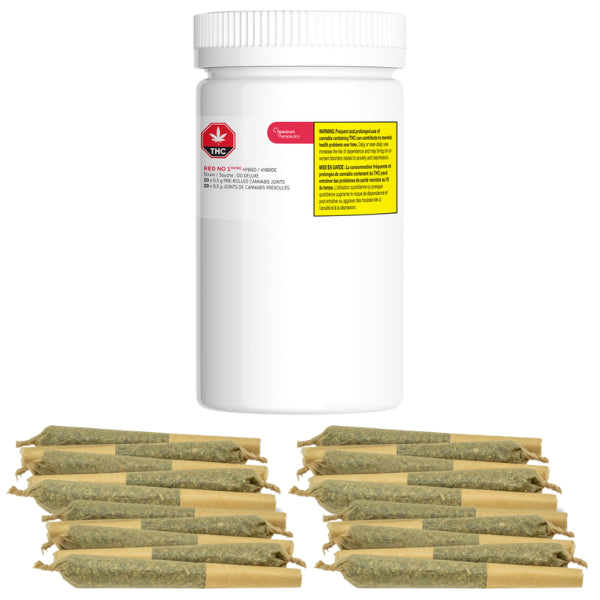
Cannabis flower is available as dried whole flowers (“bud”), milled flower (“prepared” or “ground”), and in the form of pre-rolled joints (“pre-rolls” or “Quickies”).
Whole flowers are harvested, trimmed, and then dried to a specific moisture content. Milled cannabis contains the same active ingredients as dried whole flowers and is processes to make it ready for use in a vapourizer. Pre-rolls contain milled flower in a convenient, ready-to-use form.

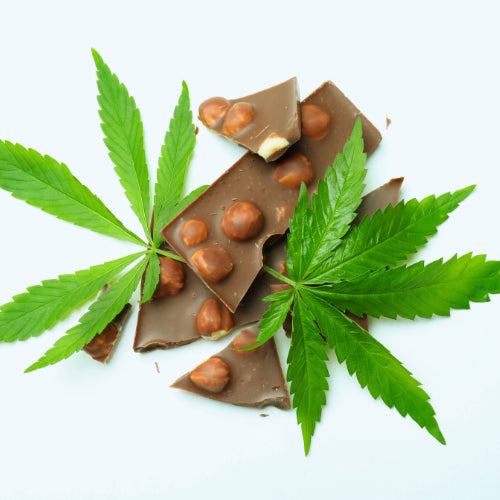
Edibles
Cannabis-infused edibles are an innovative format that is suitable for those looking for an alternative method of consuming medical cannabis. Edible products contain a consistent amount of specially formulated cannabis extract that includes THC, CBD, or a combination of both.
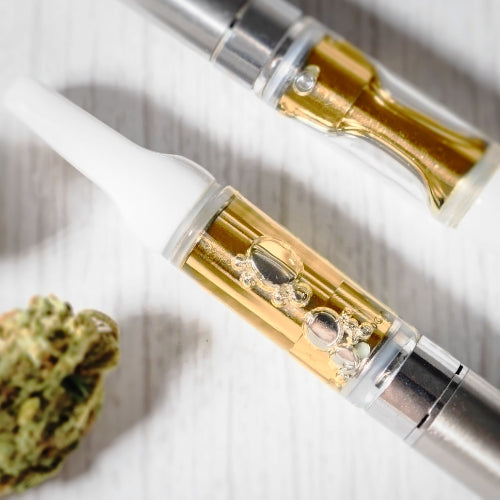
Vapourizers
Vapourizers heat cannabis flower or cannabis extract to the exact temperature required to release active compounds as vapour—without combustion, and therefore, without smoke.
There are two types of vapourizers. First, those that vapourize dried flower, such as the Storz & Bickel Volcano™ devices. Second, next-generation devices that vapourize cannabis extract and are powered by an integrated battery, such as the Tweed and Twd. 510-threaded vapes, and the Tokyo Smoke Luma™ vape system.

Beverages
Simple, familiar, and refreshing, ready-to-drink cannabis-infused beverages are changing how those with chronic conditions consume their medical cannabis. They are:
- Suitable for patients who have difficulty using inhaled medical cannabis formats or suffer from pill fatigue
- Convenient and precise, for accurate dosing
- Made in unique and easy-to-drink flavours
- Available in formulations that range from THC-dominant to balanced to CBD-dominant, to suit individual medical needs

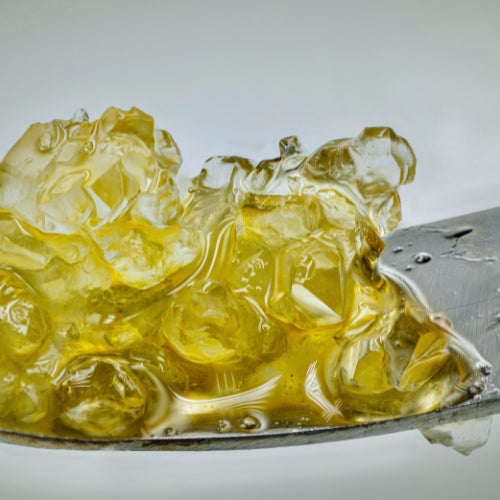
Concentrates
Both cannabis extracts (made using solvents) and cannabis concentrates (made using heat and pressure) offer a new option for those who require a fast-acting medical cannabis solution and higher levels of cannabinoids than typically available in other formats.
In fact, extracts and concentrates can range from 50%–90% THC.
Our collection of extracts and concentrates includes such offerings as live resin, live rosin, shatter, diamonds, sauce, badder, hash, and hash oil.